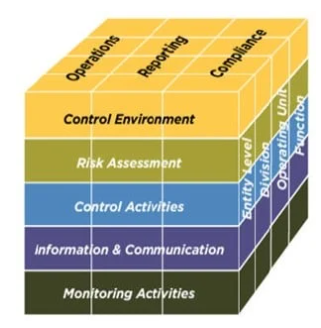
The COSO Framework
COSO stands for the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission, a private-sector initiative focused on providing thought leadership on enterprise risk management, internal control, and fraud deterrence. The COSO Framework, developed by this committee, is a widely used model for organizations to design, implement, and assess the effectiveness of their internal control systems.
Here's a more detailed breakdown:
Purpose and History:
- COSO was formed in 1985 to sponsor the National Commission on Fraudulent Financial Reporting, which studied the causes of fraudulent financial reporting.
The COSO Framework, originally published in 1992 and updated in 2013, provides a comprehensive approach to internal control.
The framework aims to help organizations improve their performance, governance, and reduce fraud.
Key Components of the COSO Framework:
- Control Environment: The foundation of internal control, including the organization's culture, values, and structure.
- Risk Assessment: Identifying and evaluating potential risks that could impact the achievement of organizational objectives.
- Control Activities: Specific policies and procedures designed to mitigate identified risks.
- Information and Communication: Ensuring that relevant information is effectively communicated to relevant parties within the organization.
- Monitoring Activities: Ongoing evaluations of the effectiveness of internal controls.
Benefits of Using the COSO Framework:
- Improved Risk Management: Helps organizations identify and manage risks effectively.
- Regulatory Compliance: Facilitates compliance with regulations like Sarbanes-Oxley (SOX).
- Enhanced Internal Controls: Provides a structured approach for developing and maintaining strong internal controls.
- Fraud Deterrence: Helps organizations prevent and detect fraud.
- Improved Operational Efficiency: Contributes to more efficient and effective business processes.