Internal Controls
Internal Controls
Internal controls are used to mitigate risk, or anything that could negatively impact UVA’s ability to meet business objectives and realize our mission. Specifically, internal controls are implemented to:
- Safeguard assets
- Verify the accuracy and reliability of accounting data and other management information
- Promote operational efficiency
- Adhere to prescribed policies and compliance with federal and state regulations
The Commonwealth Accounting Policies and Procedures (CAPP) Manual documents the policies and procedures associated with the Commonwealth's centralized accounting and financial systems. Topic No. 10305 Internal Control provides guidelines to assist state agencies and institutions in implementing internal control programs under the authority of Code of Virginia §§ 2.2-800 and 2.2-803 and identifies the Agency Risk Management and Internal Controls Standards (ARMICS) as the definitive source for internal control in the Commonwealth.
Significant Fiscal Process
To test the effectiveness of control activities and document the results, a risk assessment is completed for each significant fiscal process. A fiscal process may be considered significant if it is associated with programs or activities that:
- Consume a proportionally large share of agency resources
- Have a high degree of public visibility
- Represent areas of concern and high risk to mission-critical business processes for agency managers and stakeholders
- Have a significant effect on general ledger account balances or the financial reporting process.
Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (COSO) Framework
The COSO framework is the most broadly accepted standard for internal control in the United States and has been adopted by both federal and Commonwealth of Virginia agencies. The framework was established by a joint initiative of five private sector organizations and can be used to evaluate internal control systems. Please visit the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations (COSO) website for more information on the COSO Framework.
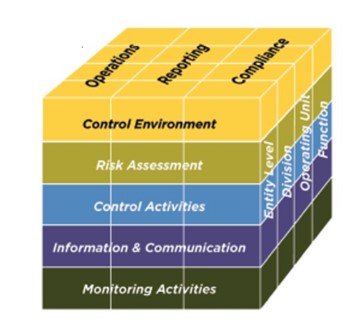
Components of the COSO Framework
The COSO Framework is comprised of seventeen principles organized within five components.
- Control Environment
- Demonstrates commitment to integrity and ethical values
- Exercises oversight responsibility
- Establishes structure, authority, and responsibility
- Demonstrates commitment to competence
- Enforces accountability
- Risk Assessment
6. Specifies suitable objectives
7. Identifies and analyzes risk
8. Assesses fraud risk
9. Identifies and analyzes significant changes
- Control Activities
10. Selects and develops control activities
11. Selects and develops general controls over technology
12. Deploys control activities through policies and procedures
- Information and Communication
13. Uses relevant information
14. Communicates internally
15. Communicates externally
- Monitoring Activities
16. Conducts ongoing and/or separate evaluations
17. Evaluates and communicates deficiencies
People
James Sullivan

Christine Kennedy